INV-17 Retinoic acid-related Orphan Receptor (ROR) Gamma Inverse Agonist
Targeting RORγ for Autoimmune Diseases and Cancer
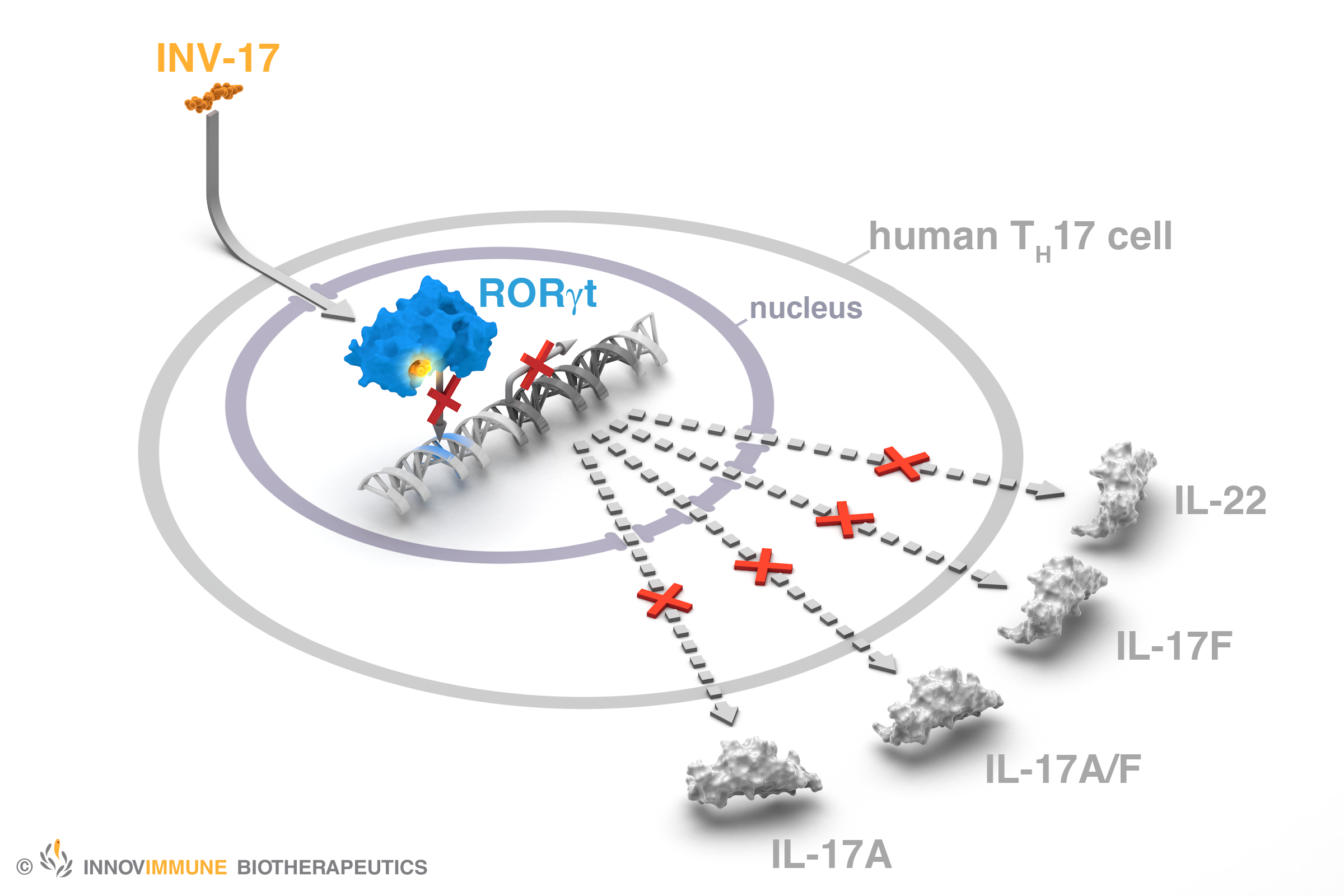
The therapeutic benefits of biologics targeting the IL-17/IL-23 pathway in autoimmune diseases implicate the importance of inhibiting T Helper 17 (Th17) cells and Th17 cytokine production. The nuclear receptor Retinoic acid receptor-related Orphan Receptor gamma (RORγ) and its immune cell-specific isoform RORγt is the master regulator of human Th17 cell differentiation and function. Blocking RORγ with oral synthetic ligands may prove to be more beneficial by completely inhibiting Th17 function and of otherwise unperturbed Th17 cytokine production by currently approved monoclonal antibodies targeting solely IL-17A and IL-23. Using structure-guided drug design, Innovimmune discovered NCE RORγ inverse agonists of the INV-17 portfolio which fully inhibit all Th17 cytokine production down to nanomolar potency. The importance of targeting RORγ may have therapeutic applications in several Th17-mediated autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. INV-17 RORγ inverse agonists have been target-validated and have demonstrated preclinical efficacy in animal models of systemic lupus erythematosus (1), multiple sclerosis (2), psoriasis (3,4) and rheumatoid arthritis (5).
Recent scientific findings have revealed an unexpected role for RORγ in regulating major oncogenic pathways contributing to stemness, aggressive behavior and tumor burden of cancer. Next-generation INV-17 RORγ inhibitors have been discovered with potent anti-tumor properties against various cancer models.
Mechanism of Action of INV-17 RORγ Inhibition
Pharmacological blockade of RORγ with oral INV-17 with its desirable selectivity, potency and favorable druggability may prove to be a novel immunomodulatory therapeutic approach for RORγ-regulated diseases. The INV-17 program is currently in clinical candidate selection phase ready to enter IND-enabling development. We are seeking to partner with biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies to advance the cross-therapeutic area clinical development of the INV-17 pipeline for multiple cancer and autoimmune disease indications with high unmet medical needs.
References:
(1) 2015 European League Against Rheumatism Congress (Rome, Italy) June 10-13, 2015
(2) 2014 Fierce Biotech. Innovimmune inhibitor prevents multiple sclerosis in mice. January 21, 2014
(3) 2017 American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meeting (Orlando, FL, USA) March 3-7, 2017
(4) 2017 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 26th Congress (Geneva, Switzerland) September 13-17, 2017
(5) 2014 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting (Boston, MA, USA) November 14-19, 2014